 In 1956 Dutch electronics giant Philips decided to see if there was a future for electronic music. It created a Studio for Electronic Music (STEM, also the Dutch word for ‘voice’) and let composers/engineers Tom Dissevelt, Dick Raaijmakers and others work there.
In 1956 Dutch electronics giant Philips decided to see if there was a future for electronic music. It created a Studio for Electronic Music (STEM, also the Dutch word for ‘voice’) and let composers/engineers Tom Dissevelt, Dick Raaijmakers and others work there.
The studio was part of Philips’ famous research facility NatLab, a name which aided Raaijmakers in finding the stagename Kid Baltan (the reverse of Dik Natlab). From 1956 to 1960 composers had access to the most sophisticated technology and used tape splicing to combine sounds into musical compositions. Raaijmakers explains on Youtube how it worked.
Somewhere during that time Edgar Varése worked for nine months at STEM on his Poème électronique.
Philips lost interest in the project. STEM was moved to the university of Utrecht and Dissevelt and Raaijmakers moved on to other projects. Today STEM lives on at the Royal Conservatoire in The Hague where Raaijmakers taught Electronic and Contemporary Music from 1966 to 1995. Last week Kid Baltan died at a retirement home in the same city at the age of 83.
(Links: Weirdomusic, NRC. Photo by Wikimedia user Rosemoon, some rights reserved.)

 A Philips ad for the company’s line of irons has been doing the rounds on the Internet.
A Philips ad for the company’s line of irons has been doing the rounds on the Internet. Dutch electronics giant Philips has sold its television division to TPV Technology from Taiwan.
Dutch electronics giant Philips has sold its television division to TPV Technology from Taiwan.
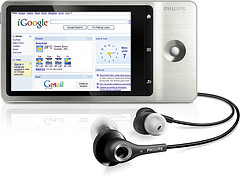 Engadget is
Engadget is 
 In 2006 I borrowed Orangemaster’s camera, hopped on the train to Eindhoven, and visited a start-up at Philips’ famous High Tech Campus to look at its single, yet to be released product, the Iliad e-reader. Today I learnt through newspaper FD that the former start-up
In 2006 I borrowed Orangemaster’s camera, hopped on the train to Eindhoven, and visited a start-up at Philips’ famous High Tech Campus to look at its single, yet to be released product, the Iliad e-reader. Today I learnt through newspaper FD that the former start-up  Consumentenbond compared the prices of making a single cup of coffee in regular households and came up with the following figures,
Consumentenbond compared the prices of making a single cup of coffee in regular households and came up with the following figures, 